Human Cell Worksheet For Kids
Looking for an engaging way to teach kids about human cells? This human cell worksheet bundle helps elementary and middle school students identify different cell types and their essential functions in the body.
From neurons that send signals to red blood cells that carry oxygen, these worksheets make learning about human biology interactive and engaging.
Perfect for both classrooms and your homeschool science curriculum, this set includes labeling exercises, matching activities, and research prompts to help students understand how cells work together to keep us healthy.
**This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate and a participant in other affiliate programs, I earn a commission on qualifying purchases.**
What’s Included in the Cell Worksheets?
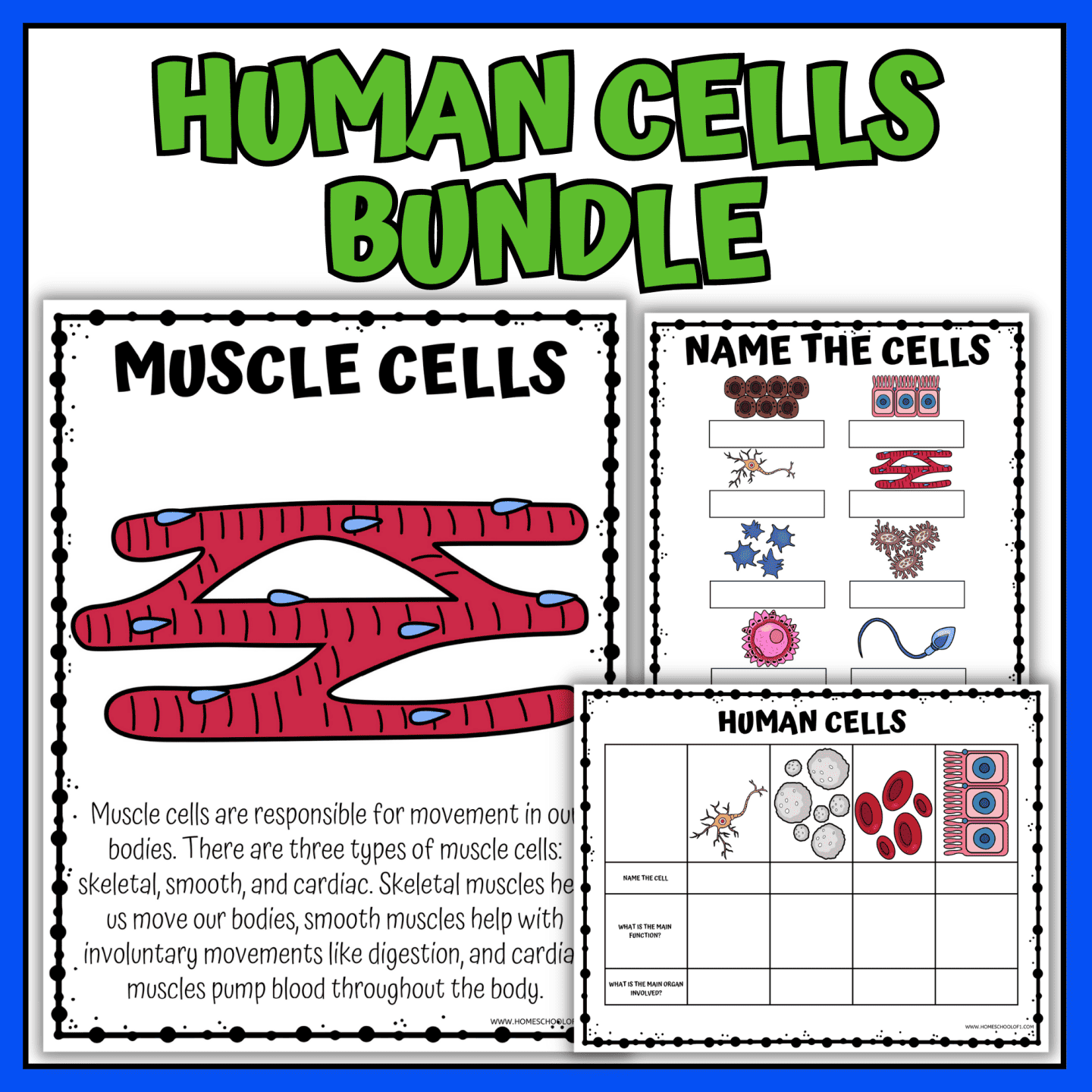
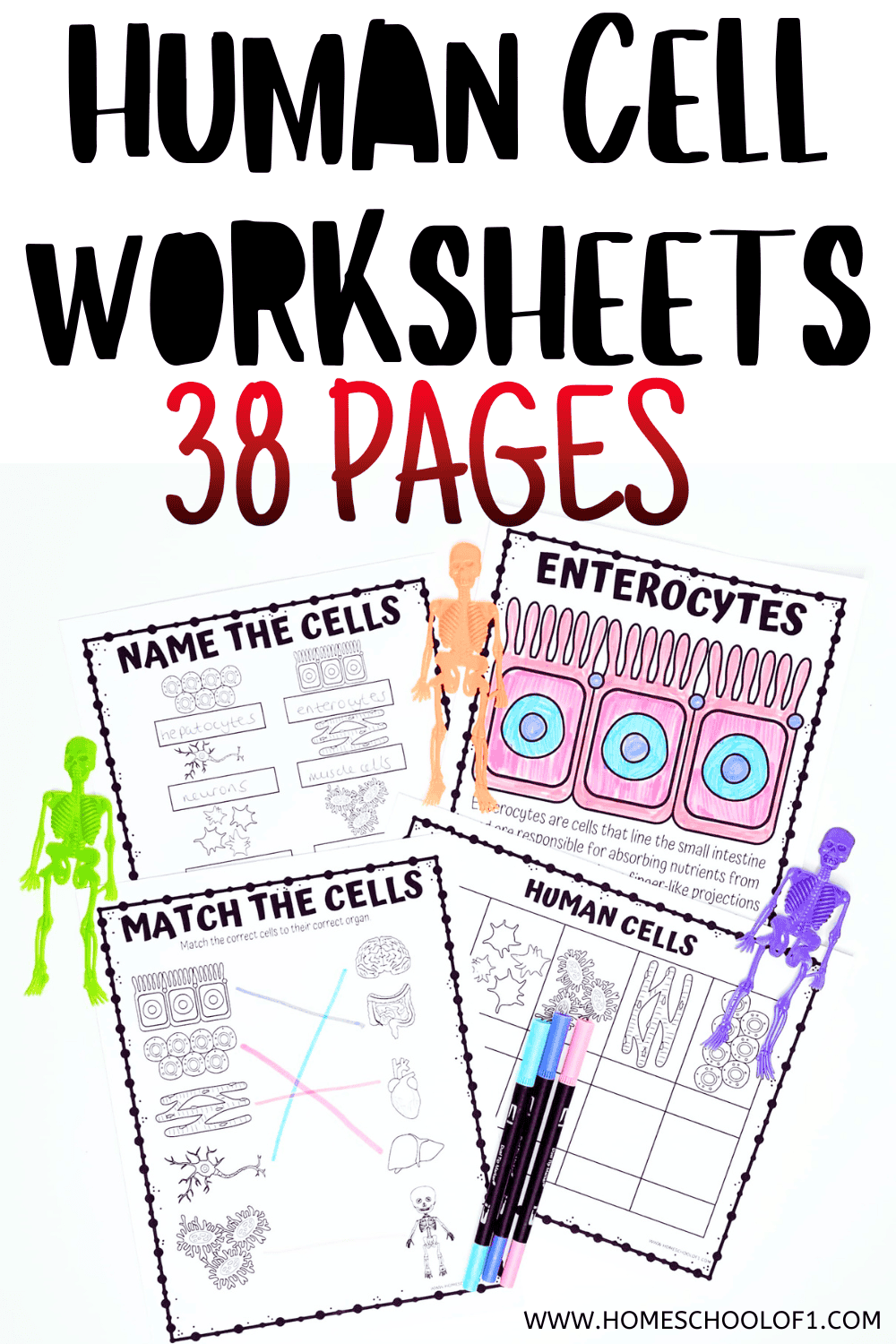
This human cells bundle includes 38 engaging pages designed for elementary and middle school students.
Here’s what’s included:
- 10 informational coloring pages – Learn about key human cells while coloring.
- 10 full-color posters – Visual aids to reinforce learning.
- Cell matching activities – Match cell names to their functions.
- Labeling worksheets – Identify different cells from a diagram.
- 3 research worksheets, where students will:
- Identify cells based on images.
- Explain the main function of each human cell.
- Determine the organ where the cell is most active.
These worksheets work great alongside our human body organs worksheets for a deeper dive into biology!
How Many Cells Are in the Human Body?
It is estimated that the human body contains around 30-37 trillion cells. However, it’s important to note that this number can vary depending on a person’s age, size, and overall health.
Additionally, the exact number of cells in the body is difficult to determine as there is no standard method for counting cells throughout the body.
Types of Human Cells and Their Functions
There are many different types of human cells, each with a unique structure and function. Here are some examples of different types of human cells:
- Muscle cells: These cells are responsible for movement and are found in the skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles.
- Nerve cells (neurons): These cells transmit electrical signals and are found in the brain, spinal cord, and throughout the body.
- Blood cells: There are three main types of blood cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells carry oxygen, white blood cells help fight infection, and platelets are involved in blood clotting.
- Skin cells: These cells make up the outermost layer of the skin and protect the body from the environment.
- Fat cells: These cells store energy and are found throughout the body.
- Bone cells: These cells make up bone tissue and are involved in bone growth and repair.
- Reproductive cells: These cells include sperm in males and eggs in females and are involved in reproduction.
Each type of cell has a specific role, working together within body systems. Pair these worksheets with our human body system worksheet to explore how cells function within organs!
Each type of cell has a specific role in the body and works together with other cells to maintain the proper functioning of organs and systems. Using human anatomy worksheets, students can visualize how these cells contribute to different body functions.
What Are the Main Human Cells?
The human cell printable focuses on key cell types that play essential roles in the body. Each type has a specific function, working together to keep us healthy.
Here are the main human cells covered in the worksheets:
- Platelets (Thrombocytes): Help with blood clotting to prevent excessive bleeding after an injury.
- Bone Cells (Osteocytes): Form and maintain bones, providing structural support.
- Neurons: Transmit electrical signals, allowing the nervous system to communicate.
- Muscle Cells (Myocytes): Enable movement through muscle contraction.
- White Blood Cells (Leukocytes): Defend the body against infections and harmful invaders.
- Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes): Carry oxygen from the lungs to tissues and remove carbon dioxide.
- Hepatocytes: The main liver cells, responsible for metabolism, detoxification, and bile production.
- Enterocytes: Found in the small intestine, they absorb nutrients from food.
- Ovum Cells (Ova): Female reproductive cells that, when fertilized, develop into embryos.
- Sperm Cells: Male reproductive cells that fertilize eggs to create new life.
More Ways to Explore the Human Body
Keep the learning going with these free printable science worksheets—perfect for reinforcing key concepts about the human body:
- Human body word search puzzle – Boost vocabulary with essential anatomy terms.
- Endocrine system labeling worksheet – Identify glands and understand their functions.
- Digestive system labeling worksheet – Learn how food is processed in the body.
- Respiratory system labeling worksheet – Explore how the lungs and airways work.
- Skeletal system labeling worksheet – Discover the bones that give our body structure.
- Nervous system labeling worksheet – Understand how the brain and nerves communicate.
Last Updated on 8 April 2025 by Clare Brown